
8th Grade Science
BENCHMARK SC.8.P.8.4
SC.8.P.8.4 Classify and compare substances on the basis of characteristic physical properties that can be demonstrated or measured: for example, density; thermal or electrical conductivity; solubility; magnetic properties; melting and boiling points; and know that these properties are independent of the amount of the sample
SC.8.P.8.3 Explore and describe the densities of various materials through measurement of their masses and volumes.
Key points to know
-Classify and/or compare substances on the basis of their physical properties and/or explain that these properties are independent of the amount of the sample.
-Describe density and/or calculate and compare the densities of various materials using the materials’ masses and volumes.
-Use of the density formula to calculate density, mass, or volume when comparing substances.
Visual Aids



BENCHMARK SC.8.P.8.5
SC.8.P.8.5 Recognize that there are a finite number of elements and that their atoms combine in a multitude of ways to produce compounds that make up all of the living and nonliving things that we encounter.
SC.8.P.8.1 Explore the scientific theory of atoms (also known as atomic theory) by using models to explain the motion of particles in solids, liquids, and gases.
SC.8.P.8.6 Recognize that elements are grouped in the periodic table according to similarities of their properties.
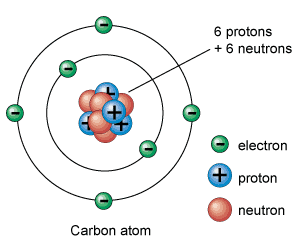
SC.8.P.8.7 Explore the scientific theory of atoms (also known as atomic theory) by recognizing that atoms are the smallest unit of an element and are composed of subatomic particles (electrons surrounding a nucleus containing protons and neutrons).
SC.8.P.8.8 Identify basic examples of and compare and classify the properties of compounds, including acids, bases, and salts.
SC.8.P.8.9 Distinguish among mixtures (including solutions) and pure substances.
Key points to know
-Describe how elements combine in a multitude of ways to produce compounds that make up all living and nonliving things
-Describe the motion of particles in solids, liquids, and/or gases.
-Explain that elements are grouped in the periodic table according to similarities of their properties.
-Explain that atoms are the smallest unit of an element and are composed of subatomic particles.
-Identify common examples of acids, bases, and/or salts.
-Compare, contrast, and/or classify the properties of compounds, including acids and bases
-Differentiate among pure substances, mixtures, and solutions.
Visual Aids


BENCHMARK SC.8.P.9.2
SC.8.P.9.2 Differentiate between physical changes and chemical changes
SC.8.P.9.1 Explore the Law of Conservation of Mass by demonstrating and concluding that mass is conserved when substances undergo physical and chemical changes.
SC.8.P.9.3 Investigate and describe how temperature influences chemical changes
Key points to know
-Students will differentiate between physical and chemical changes.
-Students will explain that mass is conserved when substances undergo physical and chemical changes, according to the law of conservation of mass.
-Students will describe how temperature influences chemical changes.
Visual Aids



BENCHMARK SC.7.P.10.1
SC.7.P.10.1 Illustrate that the Sun’s energy arrives as radiation with a wide range of wavelengths, including infrared, visible, and ultraviolet, and that white light is made up of a spectrum of many different colors.
SC.8.E.5.11 Identify and compare characteristics of the electromagnetic spectrum, such as wavelength, frequency, use, and hazards, and recognize its application to an understanding of planetary images and satellite photographs
Key points to know
-Identify, compare, and/or contrast the variety of types of radiation present in radiation from the Sun.
-Identify and/or compare characteristics of the electromagnetic spectrum.
-Identify common uses and/or applications of electromagnetic waves.
Visual Aids


BENCHMARK SC.7.P.10.3
SC.7.P.10.3 Recognize that light waves, sound waves, and other waves move at different speeds in different materials.
SC.7.P.10.2 Observe and explain that light can be reflected, refracted, and/or absorbed
Key points to know
-Describe and/or explain that waves move at different speeds through different materials.
-Explain that light waves can be reflected, refracted, and/or absorbed.
- Explain the general relative order of wave speed in different phases
Visual Aids


BENCHMARK SC.7.P.11.2
SC.7.P.11.2 Investigate and describe the transformation of energy from one form to another
SC.6.P.11.1 Explore the Law of Conservation of Energy by differentiating between potential and kinetic energy. Identify situations where kinetic energy is transformed into potential energy and vice versa.
SC.7.P.11.3 Cite evidence to explain that energy cannot be created nor destroyed, only changed from one form to another.
Key points to know
- Identify and/or describe the transformation of energy from one form to another.
- Differentiate between potential energy and kinetic energy.
- Identify and/or explain situations where energy is transformed between kinetic energy and potential energy.
- Identify and/or describe examples of the law of conservation of energy.
Visual Aids



BENCHMARK SC.7.P.11.4
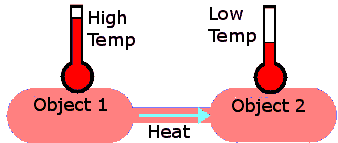
SC.7.P.11.4 Observe and describe that heat flows in predictable ways, moving from warmer objects to cooler ones until they reach the same temperature
SC.7.P.11.1 Recognize that adding heat to or removing heat from a system may result in a temperature change and possibly a change of state.
Key points to know
-Describe how heat flows in predictable ways.
-Explain that adding heat to or removing heat from a system may result in a temperature change and possibly a change of state.
Visual Aids
BENCHMARK SC.6.P.13.1
SC.6.P.13.1 Investigate and describe types of forces, including contact forces and forces acting at a distance, such as electrical, magnetic, and gravitational.
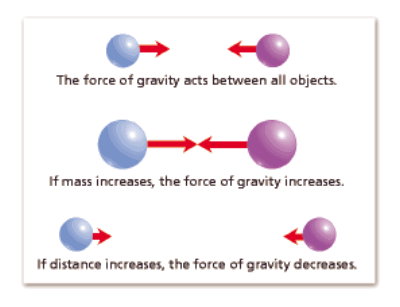
SC.6.P.13.2 Explore the Law of Gravity by recognizing that every object exerts gravitational force on every other object and that the force depends on how much mass the objects have and how far apart they are.
SC.8.P.8.2 Differentiate between weight and mass, recognizing that weight is the amount of gravitational pull on an object and is distinct from, though proportional to, mass.
Key points to know
- Identify and/or describe types of forces.
- Describe the relationship among distance, mass, and gravitational force between any two objects.
- Differentiate between mass and weight.
Visual Aids



BENCHMARK SC.6.P.13.3
SC.SC.6.P.13.3 Investigate and describe that an unbalanced force acting on an object changes its speed, or direction of motion, or both.
SC.6.P.12.1 Measure and graph distance versus time for an object moving at a constant speed. Interpret this relationship
Key points to know
- Describe and/or explain that an unbalanced force acting on an object changes its speed and/or direction.
- Interpret and/or analyze graphs of distance and time for an object moving at a constant speed.